In an era where cybersecurity threats are rapidly evolving, the Department of Defense (DoD) has recognized the need for a paradigm shift in its approach to securing information systems. This recognition has led to the adoption of the Zero Trust framework, as outlined in the DoD CIO Zero Trust strategy. This strategy is not just a technological upgrade but a fundamental change in how the DoD approaches cybersecurity, emphasizing the importance of never trusting and always verifying within its network.
Defining Zero Trust in the DoD Context
The DoD CIO defines Zero Trust as a security model that necessitates strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources on a private network, regardless of whether they are sitting within or outside of the network perimeter. This approach is critical for DoD agencies, where the protection of sensitive data and systems is paramount. In this context, Zero Trust is not just a concept but a necessary evolution in defense strategies. The following diagram outlines the fundamental pillars and components of the DoD Zero Trust capabilities.
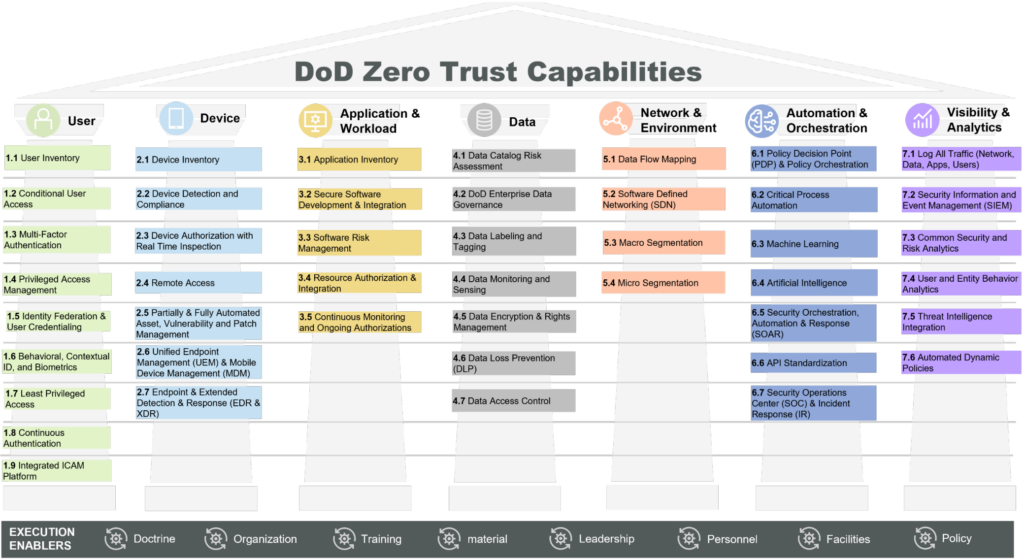
Overview of the DoD CIO Zero Trust Strategy
The DoD CIO Zero Trust strategy outlines several key goals and objectives:
- Zero Trust Cultural Adoption: Transitioning to a Zero Trust framework across the DoD.
- Secured DoD Information Systems: Operationalizing Zero Trust to enhance resilience.
- Technology Acceleration: Keeping pace with industry advancements to counter evolving threats.
- Zero Trust Enablement: Integrating Zero Trust into DoD processes for seamless execution.
These goals are fundamental to the successful implementation of Zero Trust within the DoD.
Detailed Insights into DoD’s Zero Trust Capability Structure
Following the overview of the DoD CIO Zero Trust strategy, it’s essential to delve into the specific components of the Zero Trust capability structure. These components are integral to the strategy’s implementation and success:
- Identity Verification and Management: A core tenet of Zero Trust is ensuring that every user and device is authenticated and authorized before accessing network resources. This involves robust identity verification mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication and continuous validation. For the DoD, where access to sensitive information is a matter of national security, this aspect is crucial.
- Device Security: In Zero Trust, every device is treated as a potential threat. This approach necessitates a comprehensive device security strategy, encompassing device integrity checks, security posture assessments, and real-time monitoring. The importance of this strategy for the DoD lies in safeguarding against compromised devices that could serve as entry points for attackers.
- Network Segmentation and Micro-Segmentation: The DoD’s strategy emphasizes dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit lateral movement and contain breaches. This segmentation is key in minimizing the impact of potential intrusions and ensuring that access to network resources is strictly need-based.
- Data Protection and Encryption: Protecting data at rest and in transit is a cornerstone of the Zero Trust model. The DoD’s focus on robust encryption and data tagging ensures that sensitive data is secure, regardless of its location. This strategy is vital in preventing data breaches and leakage of classified information.
- Automated Threat Detection and Response: Leveraging automation for real-time threat detection and response is another critical aspect. The use of AI and machine learning helps the DoD in quickly identifying and mitigating potential threats, a crucial capability given the scale and sophistication of cyber threats faced.
- Visibility and Analytics: Achieving comprehensive visibility into network activities and user behaviors is imperative. This enables the DoD to monitor for anomalous activities, thereby enhancing its ability to detect and respond to threats proactively.
Each of these strategies plays a vital role in fortifying the DoD’s cybersecurity posture. By meticulously implementing these components, the DoD aims to establish a robust Zero Trust ecosystem that can adapt to and counter evolving cyber threats.
KubeZT’s Alignment with DoD Zero Trust Strategy
KubeZT emerges as a compatible solution with the DoD’s Zero Trust strategy:
- Authoritative Trust Model: KubeZT’s model of a root CA with nested and federated intermediate CAs aligns well with the DoD’s identity and access management strategies, providing automated certificate management and role-based access control.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: KubeZT supports OTP and YubiKey authentication, aligning with the DoD’s emphasis on strong authentication mechanisms.
- Micro-Segmentation and Network Control: Through tools like Calico/Cilium CNI, KubeZT enables network segmentation, crucial for the DoD’s strategy of secure and controlled network environments.
- Policy Enforcement and Admission Control: KubeZT’s use of OPA for admission control aligns with the DoD’s focus on application and workload security.
- Monitoring, Logging, and Dark Net Capabilities: These features of KubeZT support the DoD’s objectives for enhanced visibility, analytics, and secure communication.
- DevSecOps and Secure Infrastructure: KubeZT’s emphasis on DevSecOps and secure infrastructure development is in line with the DoD’s requirements for resilient and responsive technology systems.
Conclusion
KubeZT stands as a pivotal tool in supporting the DoD’s transition to a Zero Trust architecture. Its features and capabilities align closely with the strategic goals and objectives set forth in the DoD CIO Zero Trust strategy. As the DoD continues to evolve its cybersecurity posture to meet emerging challenges, solutions like KubeZT will be crucial in ensuring the robustness and resilience of its defense mechanisms.








